Modeling
In these studies, we formally develop theories and system-level models about intelligent functions. This includes conceptual and mathematical theses, as well as artificial neural network development and testing.
Information Theory
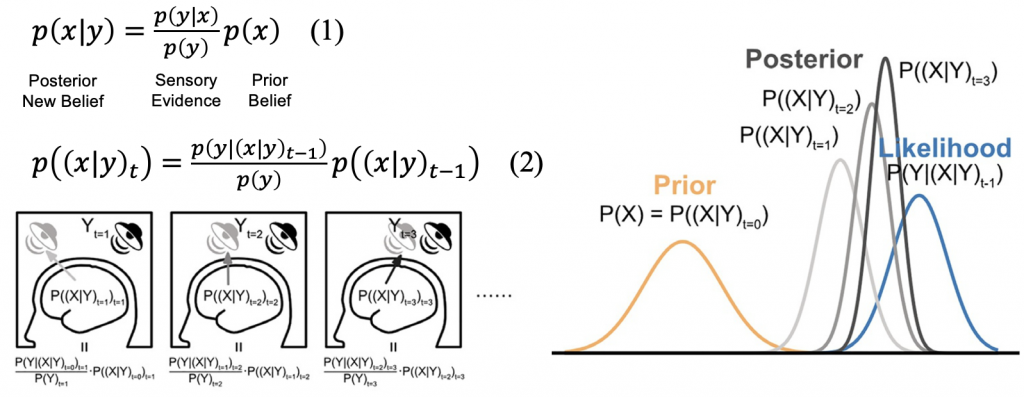
Here, we explore theoretical ideas to formalize how the brain, in its functioning, consumes information from the environment to build its structure and compute actions to interact with the environment [1]. These functions might be psychologically understood as perceptions, memories, beliefs, and predictions. One audacious aim is to arrive at an equation for intelligent functioning.
Making machines with Theory of Mind
We have ongoing work to ultimately impart a robot, given its set of sensors and actuators, with Theory of Mind (ToM) so that it is better able to interact with humans. These studies are conducted in collaboration with Prof. Li-Chen Fu from the Dept. of Elec. Eng., NTU.
ToMNet+
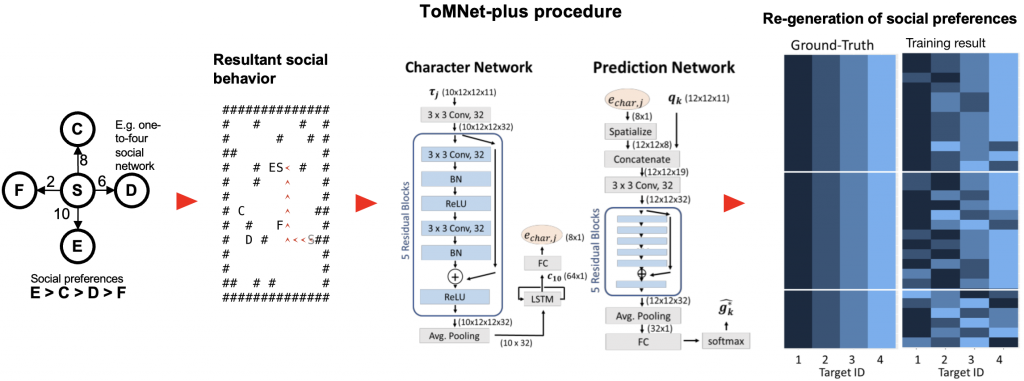
Our current completed work [2] demonstrates an artificial neural network called ToMNet-plus, which is modified from DeepMind's ToMNet. ToMNet-plus is able to represent the social preferences of an agent toward other target agents after simply observing how the source agent behaves toward the target agents. This suggests that our model could encode behavioral information in a form of conceptual graphs about simple hidden associative causal graphs that drive observed information. [url] [Github]
ToMNet 2.0
We are currently working on an enhancement based on ToMNet+, to make ToMNet 2.0 which can represent the effective social preferences of five agents toward each other.
Bibliography
- Goh, J. O. S., Hung, H.-Y., & Su, Y.-S. (2018). A conceptual consideration of the free energy principle in cognitive maps: How cognitive maps help reduce surprise. In Psychology of Learning and Motivation: Vol.69 (pp. 205–240). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.plm.2018.09.005 [url]
- Y. -S. Chuang et al., “Using Machine Theory of Mind to Learn Agent Social Network Structures from Observed Interactive Behaviors with Targets,” 2020 29th IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN), Naples, Italy, 2020, pp. 1013-1019, doi: 10.1109/RO-MAN47096.2020.9223453. [url]
